Projects | VR and AR Lab | NC State ISE
Projects
Last Updated: 12/06/2024 | All information is accurate and still up-to-date
VARL Projects
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) projects are transforming how we learn, work, and interact with technology. These cutting-edge projects create immersive experiences that blend the digital and physical worlds. VR projects fully immerse you in virtual environments, while AR projects enhance your real-world surroundings with digital information.

Scale Cognition through Advanced Learning Environments in Virtual Reality (SCALE-VR) | Projects
The Scale Worlds projects allow users to “shrink and grow”. Watch a short video on Scale Worlds below.
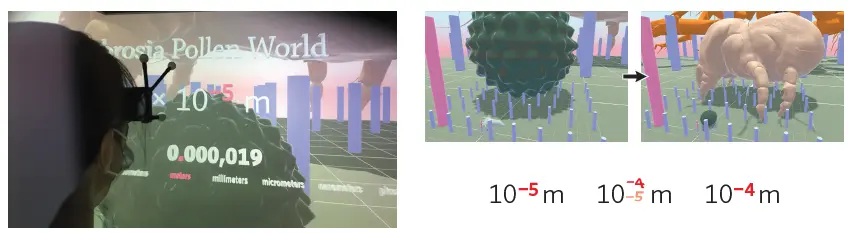
The Next Generation Science Standards propose “scale, proportion, and quantity” as a crosscutting concept that pervades science and can aid students in making connections across topics, disciplines, and grades in order to construct a more robust understanding of science. While cutting edge STEM research, such as nanotechnology and exoplanet exploration, is being conducted at extremes of scale, research shows that learners of all ages hold inaccurate ideas about the size of scientifically relevant entities.
Funded by the National Science Foundation, the SCALE-VR project aims to explore how immersive virtual environments can improve learning about scale. The project involves creating a virtual learning environment called Scale Worlds, where students can experience size comparisons that are impossible in everyday life. This project uses a Cave Automatic Virtual Environment (CAVE) to allow students to experience scale firsthand. SCALE-VR will help students better understand concepts like powers of ten, scientific notation, and measurement. Ultimately, this research will benefit STEM education by advancing techniques that apply to many math-related subjects.
Virtual Instructor Application using Augmented Reality for Worker Posture Training


Musculoskeletal disorders are the most common type of workplace injury today. To address this, we’ve developed a new training program using advanced augmented reality (AR) technology. AR allows users to see both real-world and virtual objects in the same environment. These projects are driven by the 10 Big Ideas of the National Science Foundation. We created the Virtual Instructor Application (VIA) to help workers learn safer lifting techniques. We began with the first version, VIA-1. The main goal of VIA-1 was to create an interactive platform for training manual materials handling (MMH) workers in safer postures. These postures include squat lifting, stoop lifting, and overhead reaching. With VIA-1, users can match their own body positions to the virtual instructor’s postures in AR. They can also walk around the virtual instructor, created by point-cloud technology, to observe and learn lifting techniques from different angles.
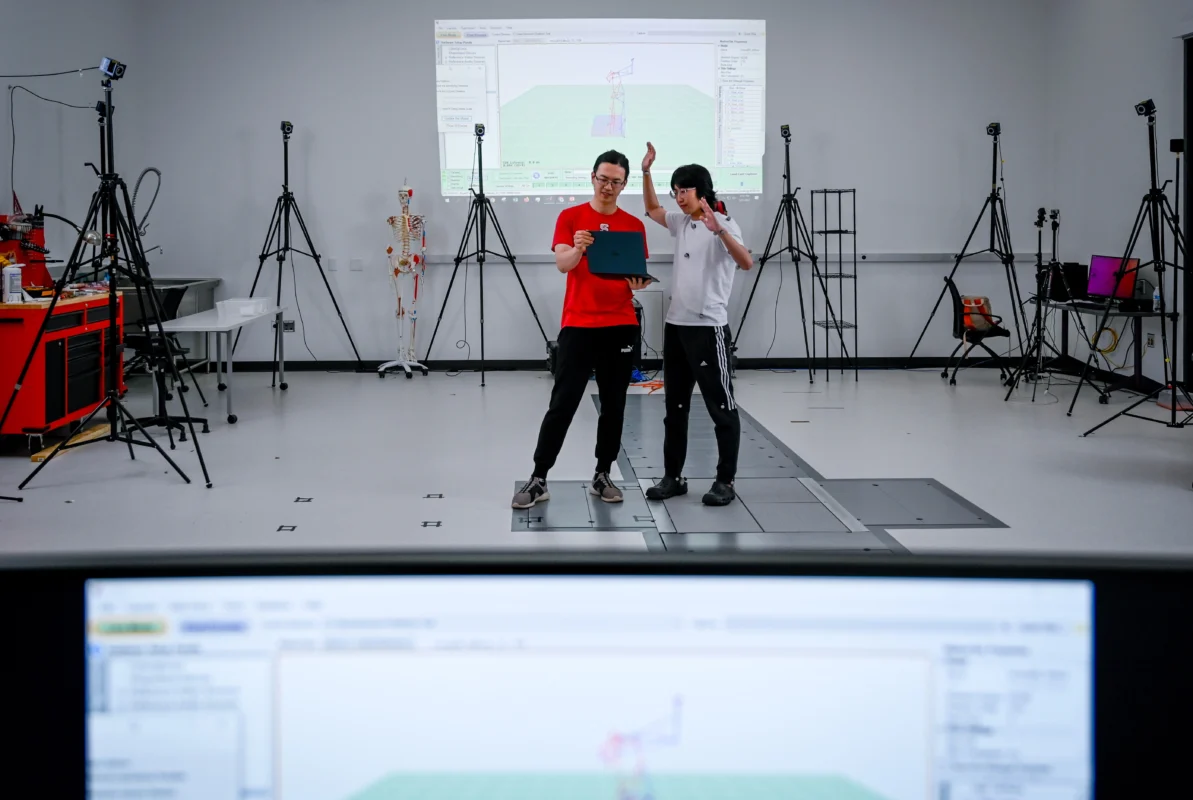
Comparison of Psychological Responses to Proximate Robot Motion Between the Physical World and an Immersive Digital Twin

Virtual reality (VR) helps simulate dangerous environments for training and psychological assessments. Digital twins, which are virtual copies of real-world environments, enable safe exploration of human-robot interactions (HRI). However, do these virtual environments accurately reflect how robot movement impacts human performance, workload, and stress? To explore this, we created a mock work-cell where participants performed a visual search task while a collaborative robot moved its arm. We then built two digital twins in VR to compare real-world effects with those in high- and low-fidelity virtual environments. We measured task performance, workload, stress, and presence. Our results showed that while task performance remained similar across all environments, subjective workload and stress were lower in virtual environments. These results suggest that human-factor evaluations in digital twins require careful interpretation.
Robot-Related Injuries in the Workplace
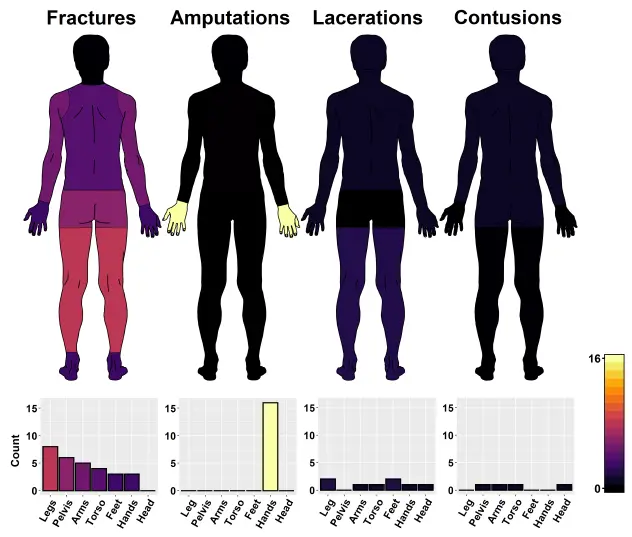
Industrial robots are becoming more common in the U.S. and around the world. However, we still don’t fully understand the extent of robot-related workplace injuries. This knowledge gap hinders the development of effective safety strategies. To address this, we analyzed Severe Injury Reports (SIRs) related to robot injuries from the U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). We identified 61 relevant reports and categorized the hazard scenarios and injuries. The two most frequent scenarios were workers being pinned, pinched, or struck by robots during maintenance activities. Most injuries resulted from constrained impacts. Finger amputations were the most common injury, followed by fractures in the extremities. These findings suggest strategies to reduce both the likelihood and severity of robot-human impacts.
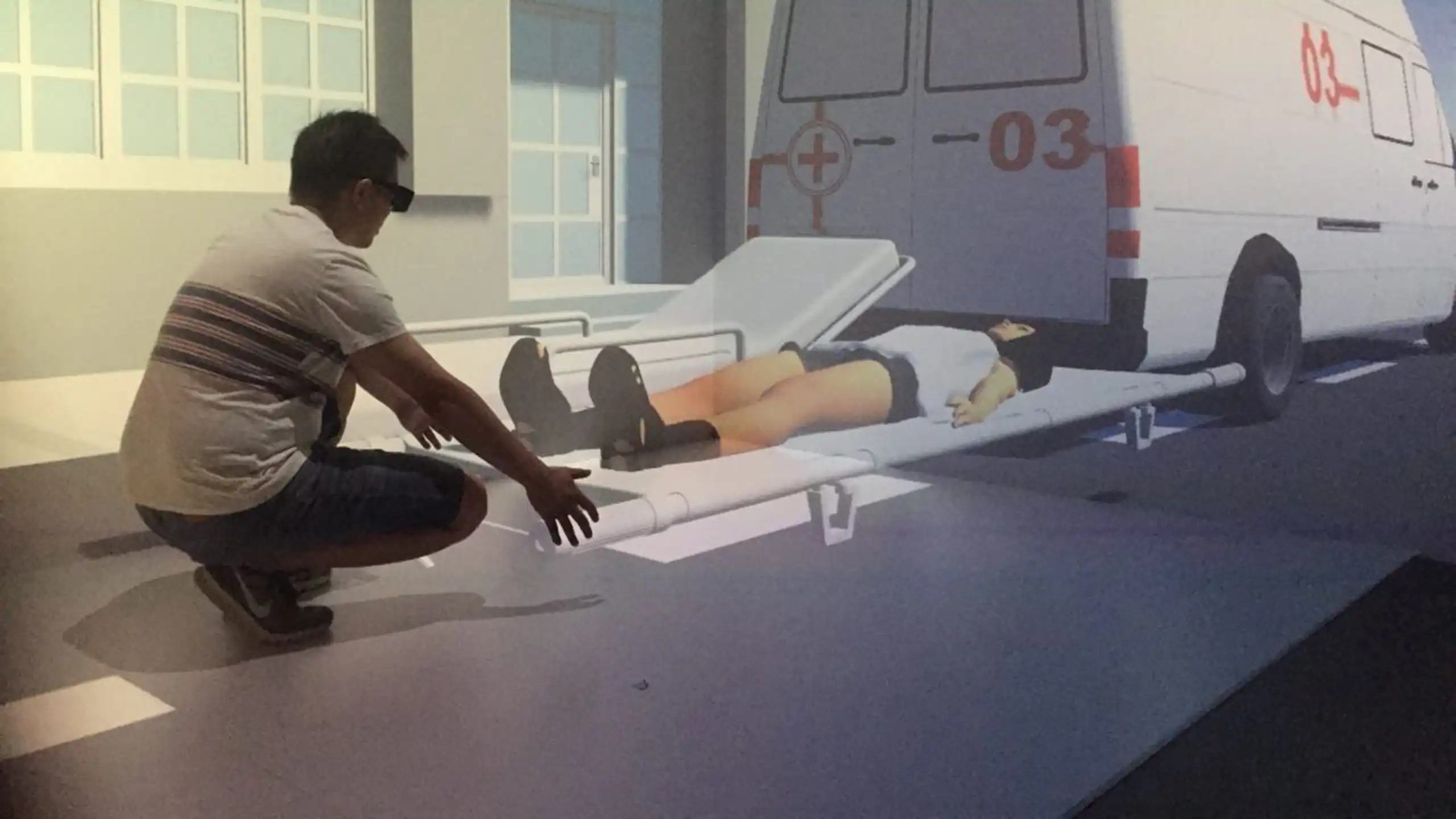
Emergency Medicine Patient Lift Training Simulation in Virtual Reality
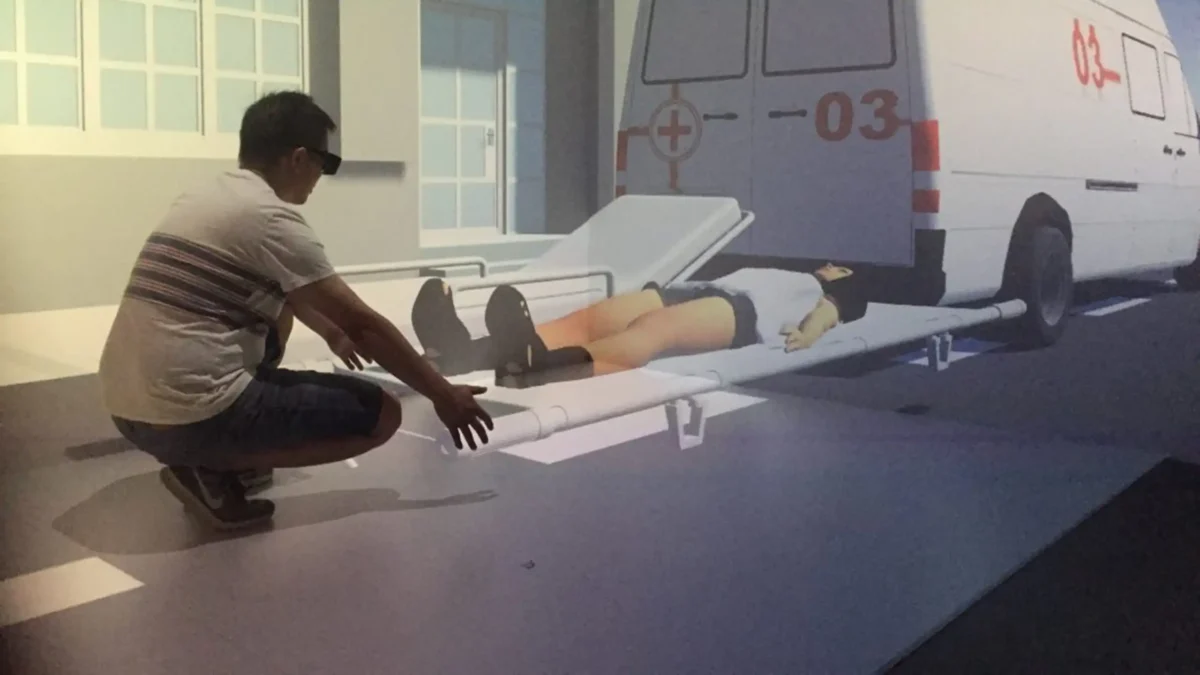

Musculoskeletal disorders are the most common type of workplace injury today. In particular, patient handling is a major cause of these injuries, especially among healthcare workers worldwide. To address this, nine participants first performed a three-part physical lift, as done in the pilot study, in order to establish virtual exertion thresholds for three different weights: 100, 150, and 200 pounds. Afterward, they completed virtual lifts in a Cave Automated Virtual Environment (CAVE). This immersive technology allows participants to practice lifting safely and without risk. By comparing both virtual and physical lifting, we can identify areas for improvement, refine techniques, and ultimately enhance worker safety.
Investigation of Virtual Reality Guided Upper Limb Exercises
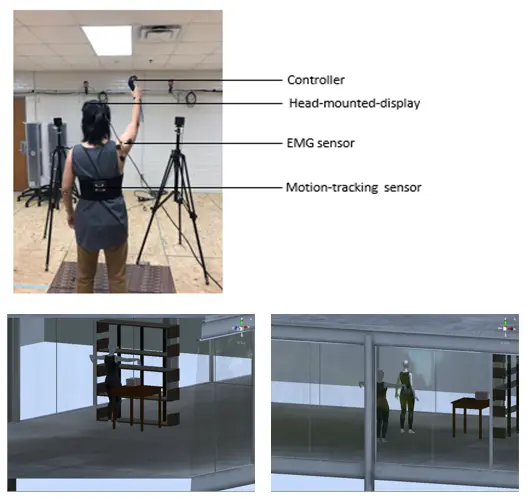

Shoulder pain is common among people with work-related musculoskeletal disorders. These disorders can be disabling, often making everyday activities difficult. While many individuals turn to traditional shoulder rehabilitation programs for help, new technologies, such as virtual reality (VR), are gaining increasing attention in physical rehabilitation. In fact, VR offers innovative ways to support recovery by providing interactive and engaging exercises. Moreover, it improves rehabilitation outcomes by offering a more personalized and dynamic approach. As a result, VR has become an exciting and effective option for those seeking alternative treatment methods.
Why Projects are Important
Research plays a crucial role in connecting and educating the community. Through research projects, we uncover new knowledge and develop innovative solutions to real-world problems. These discoveries help improve education, healthcare, and technology, benefiting everyone in the community. By sharing research findings, we create opportunities for learning and collaboration.
We’ve had the exciting opportunity to host local students and teach them about the possibilities of Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR).
Through hands-on experiences, students explore how these technologies are changing the way we learn, work, and interact with the world. By engaging with AR and VR, students gain valuable insights into emerging tech and its real-world applications.
If you’re interested in seeing how these technologies are shaping the future, check out our Outreach to learn more!
